Xpath:
Xpath in selenium is an XML path used for navigation through the HTML structure of the page, for finding any element on a web page.
There are TWO types of XPath:
1) Absolute XPath2) Relative XPath
Absolute XPath:
- This XPath has the entire path from the starting root node to the particular web element which we want to identify.- It starts with Single Slash(/).Example: /html/body/div[1]/form/div[3]/input
Relative XPath:
- This XPath starts from the Middle of the DOM Structure.- It starts with Double Slash(//).
Types of Relative Xpath Methods:
1) Basic Xpath: The common approach of writing the XPath in selenium. Which is the combination of a TagName and Attribute value.
Syntax: //TagName[@Attribute='Value']Example: //input[@id='123']
2) Using 'or' & 'and':
'or'
Syntax: //TagName[@Attribute1='value' or @Attribute2='value']
- In the above syntax there are two attributes, here if any one attribute matches with the web element then that web element will be selected.
Example: //Input[@id='123' or @class='fname']
'and'
Syntax: //TagName[@Attribute1='value' and @Attribute2='value']
- If both Attributes are matched then that web element will be selected.
Example: //input[@id='123' and @class='name']
3) starts-with Method:
It is used when the value of any attribute changes dynamically at the end of the web element.
Syntax: //TagName[starts-with(@Attribute, 'starting fixed value')]
-
Example: <div class="Transaction - 92345 67890 ">
- Here Transaction is fixed. 92345 and 67890 values will be dynamically changing.- So XPath will be : //div[starts-with(@class,'Transaction')]
4) ends-with Method:
it is used when the value of any attribute changes dynamically at the start of the web element.
Syntax: //TagName[ends-with(@Attribute, 'ending fixed value')]
-
Example: <div class=" testing college - blogger ">
- Here "- blogger" is fixed. testing and college will be dynamically changing.- So XPath will be: //div[ends-with(@class,'blogger')]
5) Contains Method:
The contains method can find the element with partial text.
Syntax: //TagName[contains(@Attribute, 'partial value')]
Example: <div class="automationtesting">
Then Xpath will be: //div[contains(@class, 'tion')]
6)text Method:
By using this text(), we find the element with an exact text match(Visible text).
Syntax: //TagName[text()='visibleText'] or //*[text()='visibleText']
Example: //*[text()='Gmail']
7) Contains + text Methods:
Combining these two methods we can use partially visible text to select a web element.
Syntax: //TagName[contains(text(),'partialText')]
Example: //a[contains(text(),'tion')]
XPath Axes Methods:
1) following
Syntax: //*[@Attribute='value']//following::tagName[index]
Example: //div[@id='testing']//following::div
2) following-sibling
Syntax: //*[@Attribute='value']//following-sibling::tagName[index]
Example: //ul[@class='testing']//following-sibling::li
3) parent(one parent)个:
Syntax: //*[@Attribute='value']//parent::tagName[index]
Example: //li[@id='list']//parent::ul
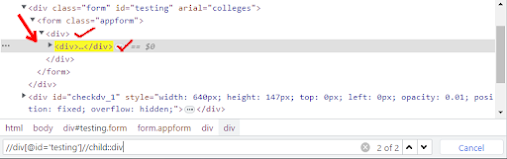
4) child:
Syntax: //*[@Attribute='value']//child::tagName[index]
Example: //div[@id='testing']//child::div
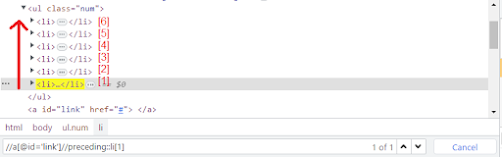
5) preceding个:
Syntax: //*[@Attribute='value']//preceding::tagName[index]
Example: //a[@id='link']//preceding::li[index]
6) ancestor个:
Selects all ancestors (parent, grandparent, etc.) of the current node.
Syntax: //*[@Attribute='value']//ancestor::tagName[index]
Example: //
7) descendant:
Select all descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) of the current node.
Syntax: //*[@Attribute='value']//descendant::tagName[index]
Example: //









No comments:
Post a Comment